| Name | Retapamulin |
| Classes |
Antiinfective Agent Antibiotic Dermatological/Topical Agent Topical Antiinfective Agent |
| Diseases |
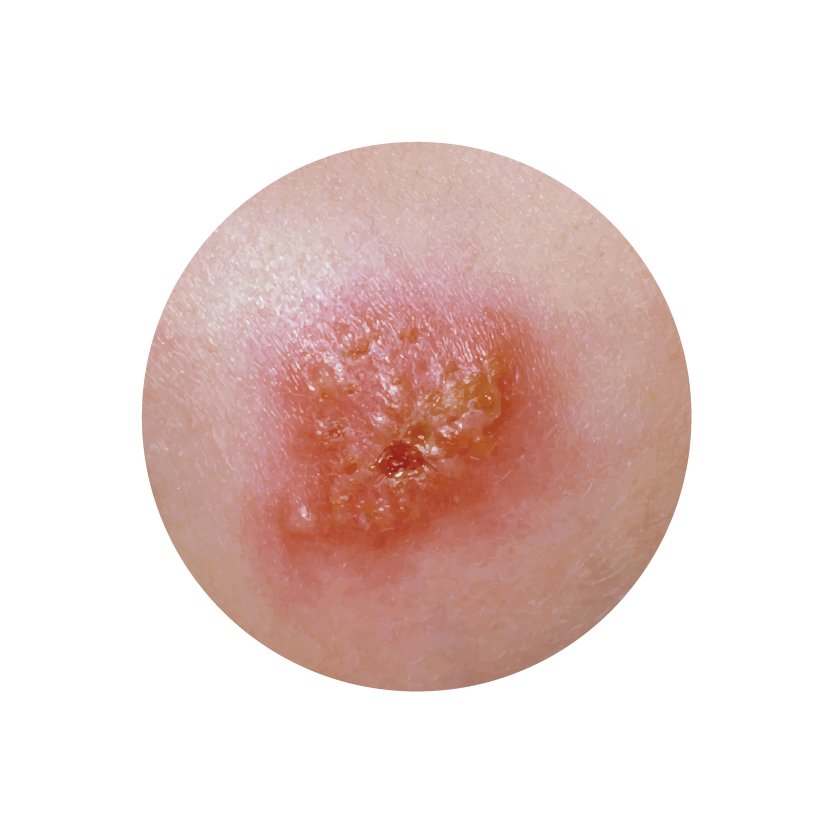
Impetigo Skin Disorder |
Retapamulin
Retapamulin is a topical antibacterial drug. Retapamulin inhibits bacterial protein synthesis by binding to a specific site on the 50S subunit of the bacterial ribosome, thus preventing the formation of new bacterial proteins.
Retapamulin ointment is indicated for the topical treatment of impetigo caused by susceptible strains of Staphylococcus aureus (methicillin-susceptible strains) and Streptococcus pyogenes in patients aged 9 months and older.
- For topical use only.
- Apply a thin layer of retapamulin ointment to the affected area twice daily for 5 days.
- The ointment should be gently rubbed into the skin until it disappears.
- The treated area should not be covered with occlusive dressings.
The most common adverse reactions (≥1%) reported in clinical trials include:
- Application site irritation
- Application site pruritus (itching)
- Application site pain or discomfort
- Hypersensitivity: Discontinue use if a hypersensitivity reaction occurs and initiate appropriate therapy.
- Non-susceptible organisms: Prolonged use may result in overgrowth of non-susceptible organisms, including fungi. If secondary infection occurs during treatment, appropriate alternative therapy should be considered.
- Eye contact: Avoid contact with the eyes. If accidental eye exposure occurs, rinse thoroughly with water.
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding: There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant or breastfeeding women. Use retapamulin during pregnancy or breastfeeding only if clearly needed.
Contraindication
etapamulin is contraindicated in individuals with a history of hypersensitivity to retapamulin or any component of the ointment.
None known.
None known.
 Bangla
Bangla English
English