| Name | Ampicillin Trihydrate |
| Classes |
Antiinfective Agent Antibiotic Penicillin |
| Diseases |
Black Lesion Breathing Problem Coughing Infectious Disease Meningitis Sinusitis UTI (Urinary Tract Infection) |
Ampicillin Trihydrate
Ampicillin trihydrate is a semi-synthetic penicillin belonging to the class beta lactam antibiotics. It exerts its action by inhibiting cell wall synthesis of susceptible organisms. It is effective against both gram positive and gram negative strains.
Ampicillin is indicated for-
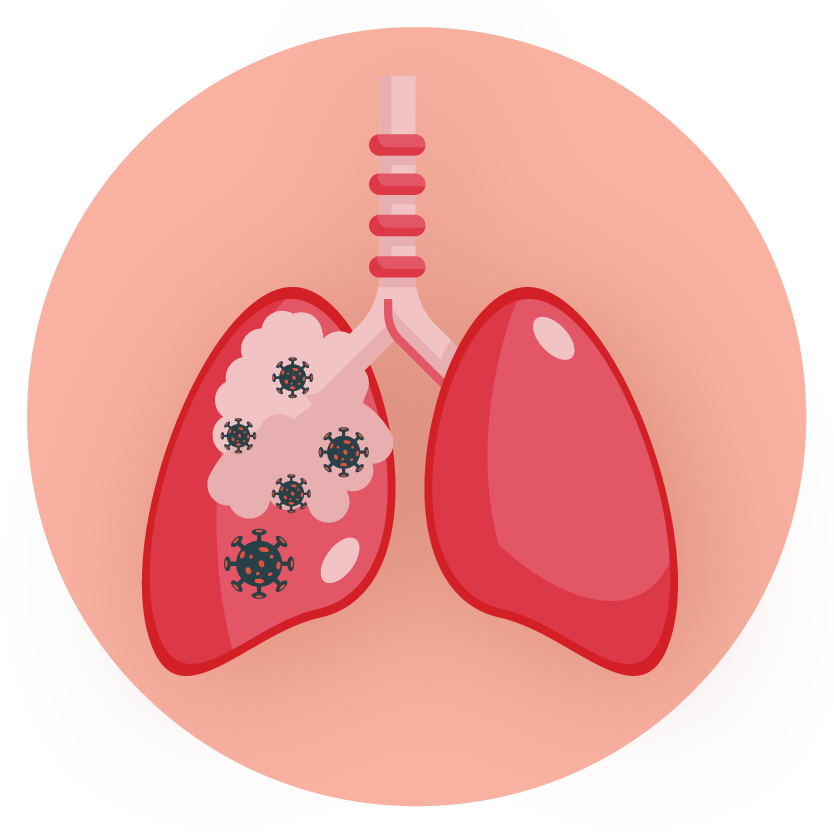
- Respiratory Tract Infections caused by S. pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus (penicillinase and non penicillinase-producing), H. influenzae and Group A beta-hemolytic Streptococci.
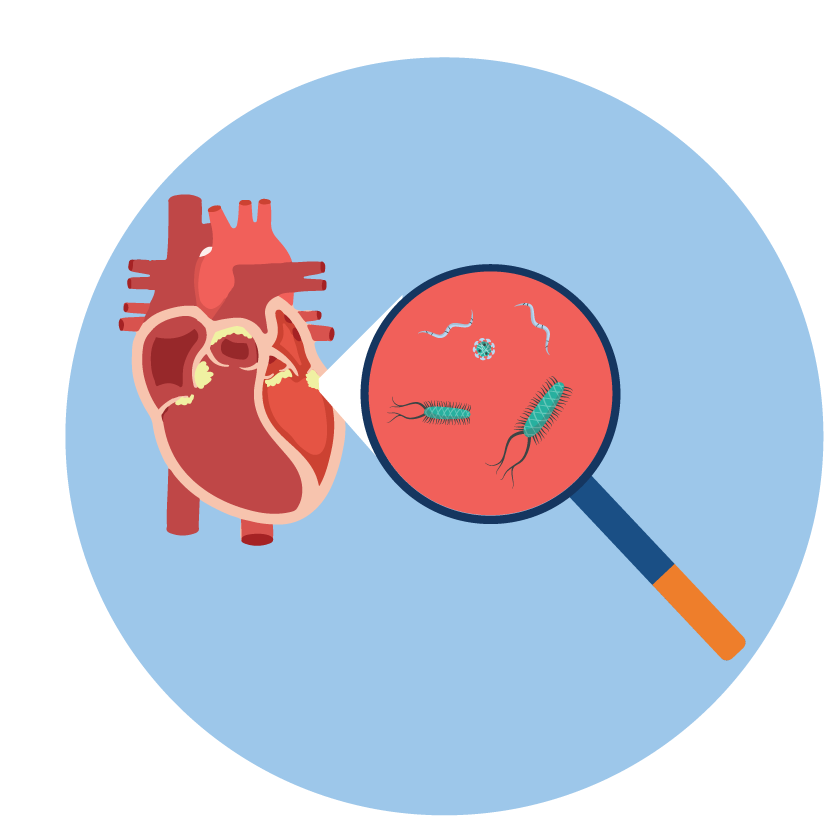
- Bacterial Meningitis caused by E. coli, Group B Streptococci, and other Gram-negative bacteria (Listeria monocytogenes, N. meningitidis).
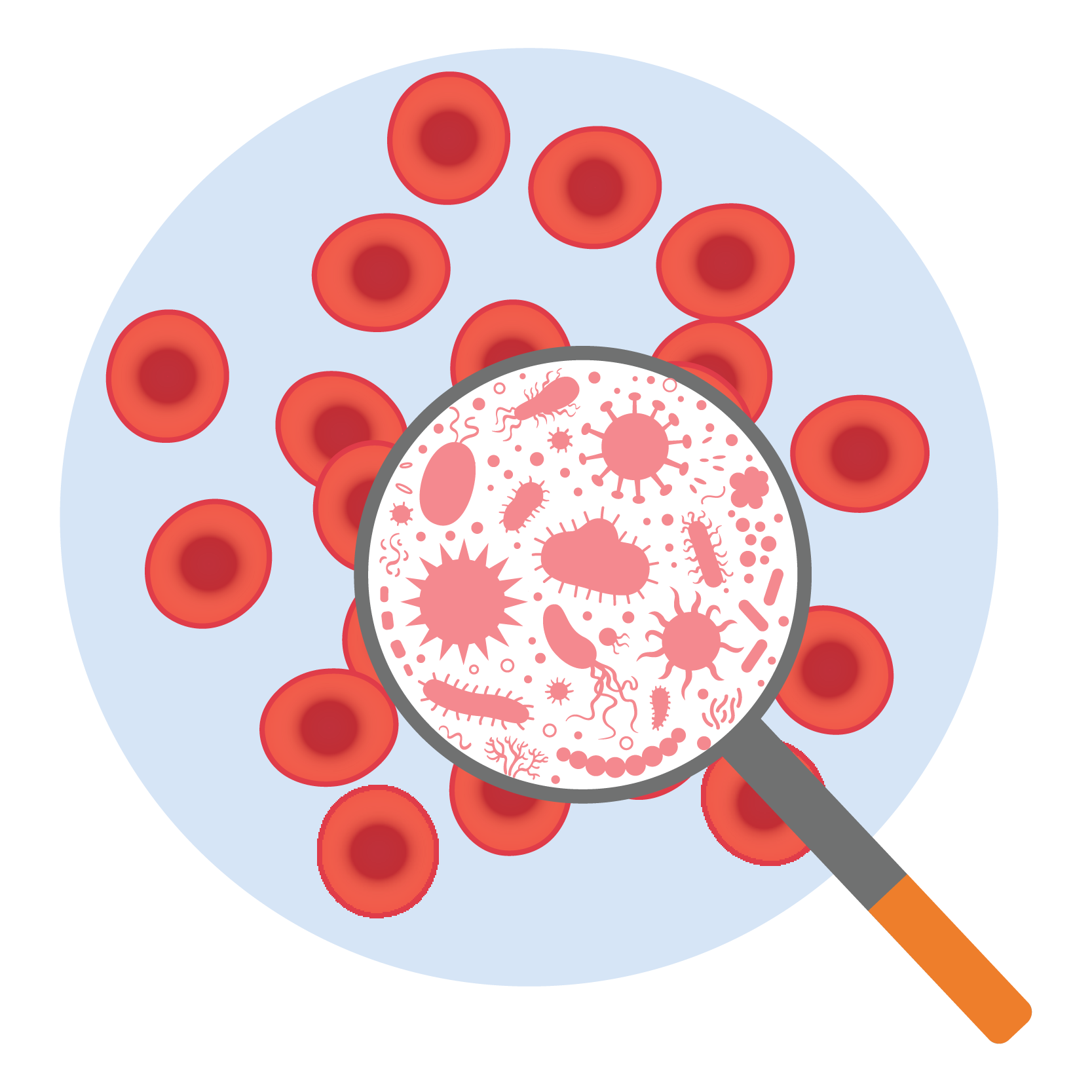
- Septicemia and Endocarditis caused by susceptible organisms.
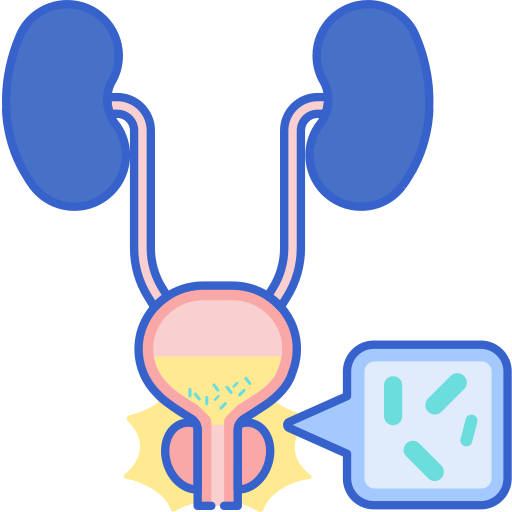
- Urinary Tract Infections caused by sensitive strains of E. coli and Proteus
mirabilis. - Gastrointestinal Infections caused by Salmonella typhi, other Salmonella spp. and Shigella spp.
The usual dose for ampicillin trihydrate is 500mg per day but can vary depending upon the type and severity of the infection.
Some patients may show hypersensitivity reactions to ampicillin. In such cases treatment should be stopped immediately.
Contraindication
- Ampicillin is contraindicated in patients with known allergy to any drug of the beta lactam class of antibiotics.
- The concurrent administration of allopurinol and ampicillin increases substantially the incidence of skin rashes in patients receiving both drugs as compared to patients receiving ampicillin alone.
- Patients with insufficient creatinine clearance may require dose adjustment.
There is no known contraindications of ampicillin trihydrate in terms of food and drinks.
 Bangla
Bangla English
English