| Name | Sulfapyridine |
| Classes |
Antiinfective Agent Antibiotic Sulfonamide |
| Diseases |
Herpetiformis (Duhring's Disease) Infectious Disease Pustular Dermatosis (Sneddon-Wilkinson Disease) Pyoderma Gangrenosum |
Sulfapyridine
Sulfapyridine is a sulfonamide antibiotic. It is a competitive inhibitor of the bacterial enzyme dihydropteroate synthetase.
For the treatment of
- Dermatitis herpetiformis
- Benign mucous membrane pemphigoid
- Pyoderma gangrenosum
For each patient, the sulfapyridine dose will be different. Follow the doctor's orders or the label's instructions. Only the average sulfapyridine doses are included in the following data. If the dose differs, do not alter it unless the doctor instructs to.
- Adults and adolescents with dermatitis herpetiformis should take 250 mg to 1 gram four times a day until symptoms improve. After the symptoms have improved, reduce the dose by 250 to 500 milligrams every three days until no symptoms remain; this dose should be taken once day.
- Children: Using this product is not advised because children rarely develop this ailment.
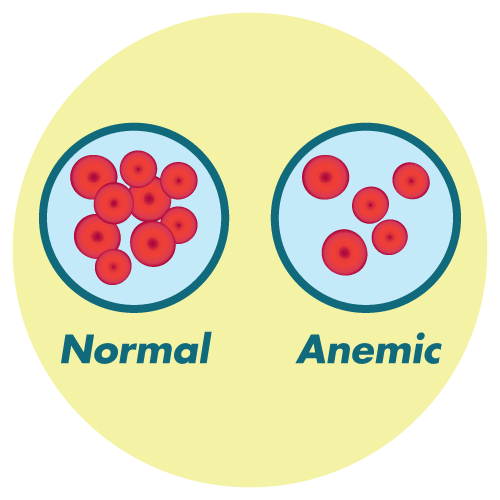
- It's critical that the doctor monitors the patient’s development on a frequent basis. Sulfapyridine might cause blood issues if taken for an extended period of time.
- Sulfapyridine has the potential to cause blood disorders. These issues can lead to an increased risk of certain infections, poor healing, and gum bleeding. As a result, when using ordinary toothbrushes, dental floss, or toothpicks, be cautious. Dental work should be postponed until blood counts have stabilized
- Sulfapyridine may make skin more susceptible to the sun than it normally is. Even brief exposure to sunlight can result in a skin rash, irritation, redness or other discoloration of the skin, or a serious sunburn.
- When you first start taking sulfapyridine, one should:
-
- If at all possible, avoid direct sunlight between the hours of 10:00 a.m. and 3:00 p.m.
- Wear protective gear, such as a hat. Wear sunglasses as well.
- Apply a sunblock with a skin protection factor (SPF) of at least 15 to the skin. Some individuals, especially those with fair skin, may require a product with a higher SPF value.
- Consult with a local health care provider if there are any questions about this.
Contraindication
It is contraindicated in patients hypersensitive to the medicine itself or other sulphonamides such as-
There's no known contraindications of the drug in terms of food and drinks.
Contraindicated in-
- Pregnancy
- Lactation
- Blood and lymphatic system disorders
- Nutritional disorders
- Severe renal or hepatic failure.
- Acute porphyria.
- Jaundice or blood disorders.
- Neonates
 Bangla
Bangla English
English