| Name | Eslicarbazepine Acetate |
| Classes |
Central Nervous System Agent Anticonvulsant / Antiepileptic Agent Psychotherapeutic Agent |
| Diseases |
Mental Disorder Seizure |
Eslicarbazepine Acetate
Eslicarbazepine acetate is an anticonvulsant drug belonging to the dibenzazepine carboxamide class. Its mechanism of action involves blocking voltage-sensitive sodium channels, which stabilizes neuronal membranes and reduces the frequency of seizures.
- Adult Patients: The recommended initial dosage of Eslicarbazepine acetate is 400 mg once daily. For some patients, treatment may be initiated at 800 mg once daily if the need for seizure reduction outweighs an increased risk of adverse reactions. Increase the dose in weekly increments of 400 mg to 600 mg once daily, based on clinical response and tolerability, to a recommended maintenance dosage of 800 mg to 1600 mg once daily.
- Pediatric Patients: The recommended dosage of Eslicarbazepine acetate is based on body weight and is administered orally once daily. Increase the dose in weekly intervals based on clinical response and tolerability, to the recommended maintenance dosage.
- Moderate or Severe Renal Impairment: Reduce dosage by 50%.
- Suicidal Behavior and Ideation: Monitor for suicidal thoughts or behavior. (5.1)
- Serious Dermatologic Reactions, Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS), Anaphylactic Reactions and Angioedema: Monitor and discontinue if another cause cannot be established.
- Hyponatremia: Monitor sodium levels in patients at risk or patients experiencing hyponatremia symptoms.
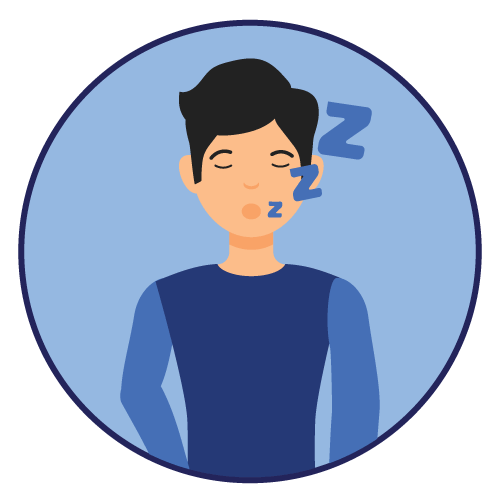
- Neurological Adverse Reactions: Monitor for dizziness, disturbance in gait and coordination, somnolence, fatigue, cognitive dysfunction, and visual changes. Use caution when driving or operating machinery.
- Withdrawal of Eslicarbazepine: Withdraw Eslicarbazepine gradually to minimize the risk of increased seizure frequency and status epilepticus.
- Drug Induced Liver Injury: Discontinue Eslicarbazepine in patients with jaundice or evidence of significant liver injury.
- Hematologic Adverse Reactions: Consider discontinuing.
Contraindication
Contraindicated in patients who are hypersensitive to eslicarbazepine acetate or oxcarbazepine.
None known.
None known.
 Bangla
Bangla English
English