| Name | Erythromycin Thiocyanate |
| Classes |
Dermatological/Topical Agent Topical Antiinfective Agent Antiacne Agent |
| Diseases |
Infectious Disease Pharyngitis Pneumonia |
Erythromycin Thiocyanate
Erythromycin is a macrolide antibiotic. It is a broad spectrum antibiotic that binds to the 50s subunit of the bacterial ribosome and inhibits its protein synthesis.
Erythromycin is indicated for the following infections-
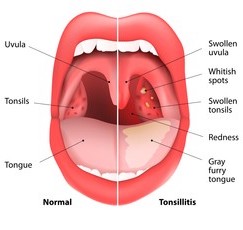
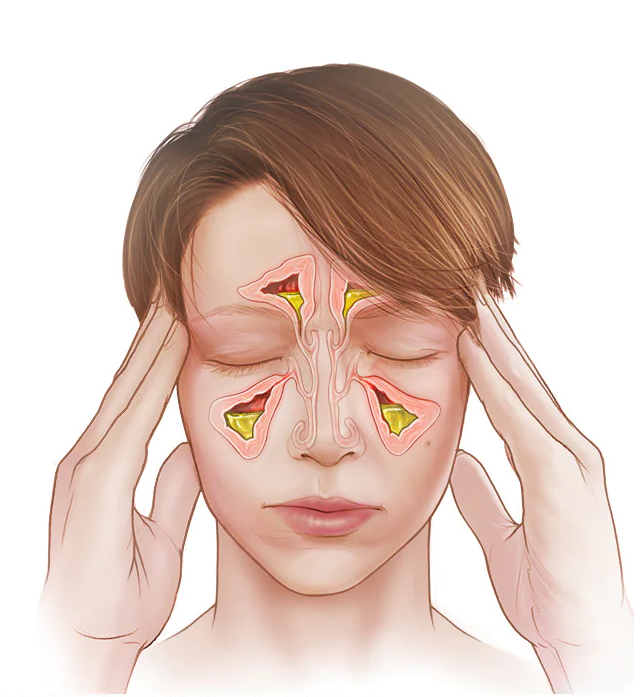
- Upper & lower respiratory tract infections- Tonsilitis, Laryngitis, Sinusitis, Bronchitis, Whooping cough.
- Ear infections.
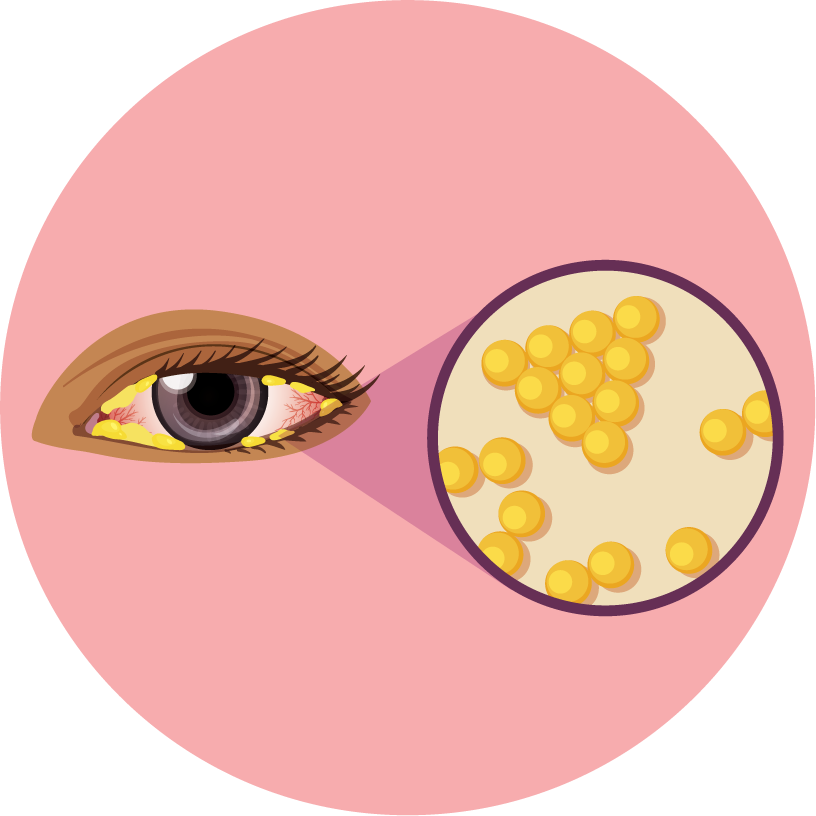
- Eye infections.
- Skin infections
- Gastrointestinal infections
- Surgical prophylaxis
For mild to moderate infections, the recommended dose is 250-500 mg every six hours. In severe cases, this may be raised to 4 gm or more every day.
The side effects of erythromycin is usually mild and resolve without the need of terminating the treatment. The most common side effects are-
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Allergic reactions
- Long term use of erythromycin can induce Long QT syndrome.
Erythromycin can cause hepatotoxicity. Rhabdomyolysis with or without renal impairment has been reported in seriously ill patients receiving erythromycin concomitantly with lovastatin.
Contraindication
- Erythromycin is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to this antibiotic.
- Erythromycin is contraindicated in patients taking terfenadine, astemizole, cisapride, pimozide, ergotamine, or dihydroergotamine
There is no known contraindication of erythromycin in terms of food & drinks.
Erythromycin should not be prescribed tp patients with underlying liver diseases and heart conditions like arrythmia.
 Bangla
Bangla English
English