| Name | Colchicine |
| Classes |
Metabolic Agent Antigout Agent |
| Diseases |
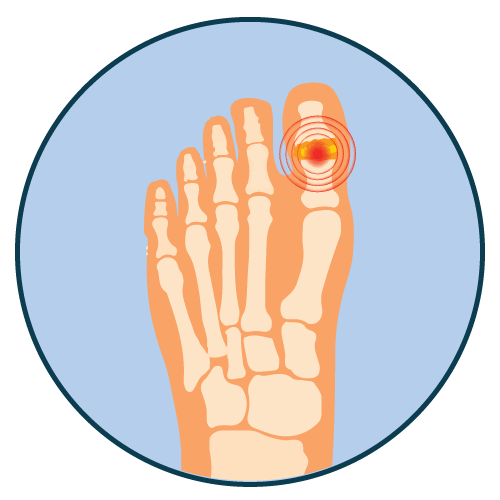
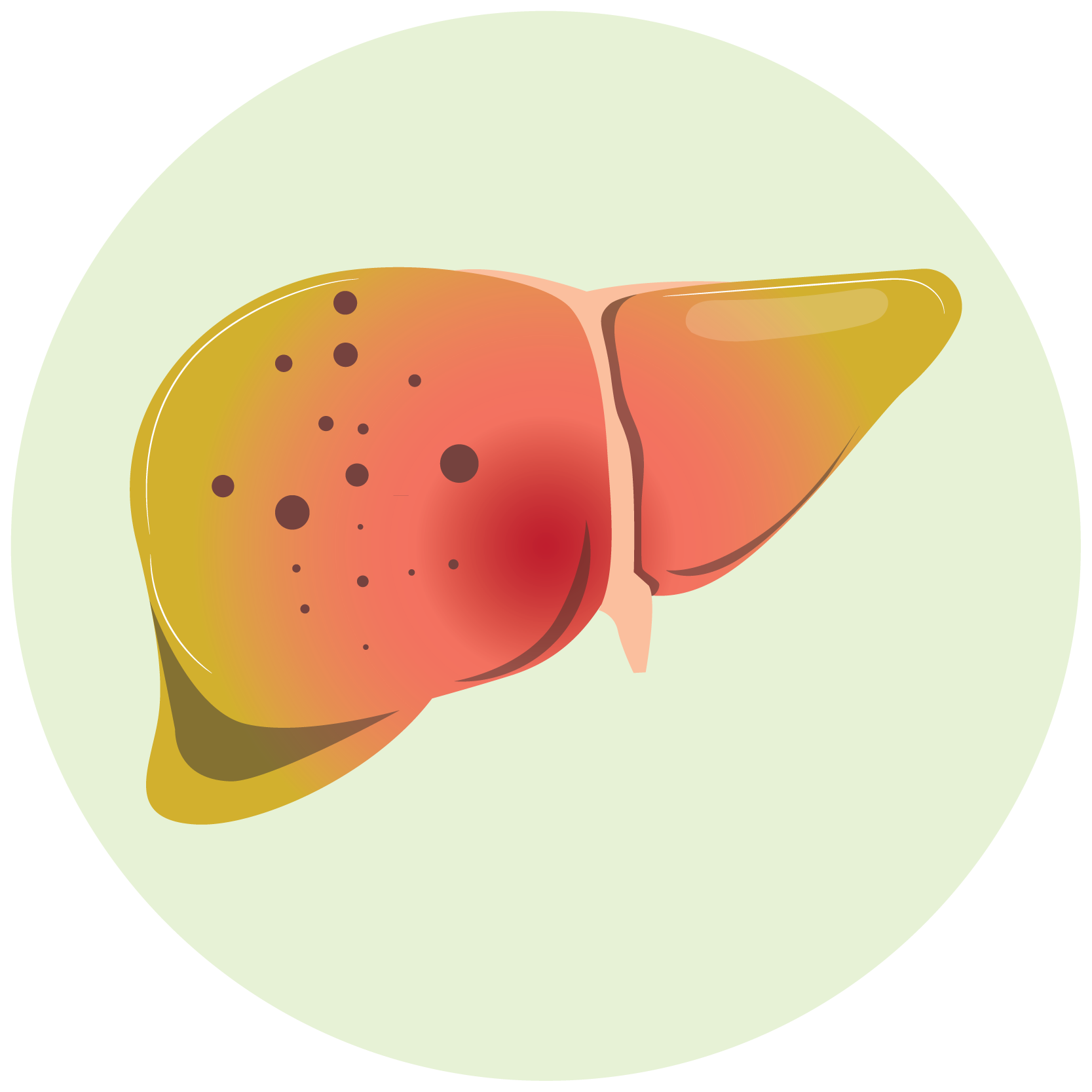
Cirrhosis Familial Mediterranean Fever (FMF) Gout Metabolic Disorder |
Colchicine
Colchicine is an alkaloid medication derived from the autumn crocus plant. The exact way in which Colchicine produces its positive results in individuals with FMF is not completely understood. Nevertheless, research suggests that colchicine may obstruct the formation of the inflammasome complex within neutrophils and monocytes that activates interleukin-1β. Furthermore, colchicine disturbs the functioning of the cytoskeleton by impeding the polymerization of β-tubulin into microtubules. This action stops the activation, release of granules, and movement of neutrophils, which are believed to contribute to certain symptoms of gout.
Colchicine tablets are indicated for:
- Prophylaxis and treatment of gout flares in adults
- Familial Mediterranean fever (FMF) in adults and children 4 years or older
The recommended dose of colchicine for the prophylaxis of gout is 0.6 mg once or twice daily, depending on the patient's age and renal function. The dose may need to be adjusted in patients with renal impairment. For the treatment of FMF, the recommended dose is 1.2 to 2.4 mg daily, depending on the patient's age and weight. Colchicine should be taken with food to reduce the risk of gastrointestinal side effects.
The most common adverse reactions associated with colchicine include gastrointestinal side effects such as-
- nausea
- vomiting
- abdominal pain
- diarrhea
In rare cases, it can also cause myelosuppression and neuromuscular toxicity. Allergic reactions, including anaphylaxis and angioedema, have also been reported.
- Fatal overdoses have been reported with colchicine in adults and children. Keep Colchicine out of the reach of children.
- Blood dyscrasias: myelosuppression, leukopenia, granulocytopenia, thrombocytopenia and aplastic anemia have been reported.
- Monitor for toxicity and if present consider temporary interruption or discontinuation of colchicine (5.2, 5.3, 5.4, 6, 10).
- Drug interaction P-gp and/or CYP3A4 inhibitors: Coadministration of colchicine with P-gp and/or strong CYP3A4 inhibitors has resulted in life-threatening interactions and death.
- Neuromuscular toxicity: Myotoxicity including rhabdomyolysis may occur, especially in combination with other drugs known to cause this effect. Consider temporary interruption or discontinuation of Colchicine.
Contraindication
- Colchicine is contraindicated in patients with hypersensitivity to colchicine or any of its components.
- Colchicine should not be used concomitantly with P-glycoprotein inhibitors or strong CYP3A4 inhibitors, as this can increase the risk of toxicity such as-
None known.
Colchicine should not be used in patients with severe renal or hepatic impairment.
 Bangla
Bangla English
English