| Name | Butenafine |
| Classes |
Antiinfective Agent Dermatological/Topical Agent Topical Antiinfective Agent Antifungal Agent |
| Diseases |
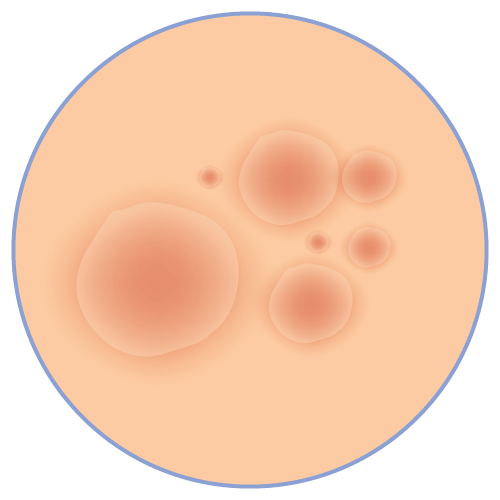
Athelet's Foot Dermatological Infection Jock Itch Ring Worm |
Butenafine
Butenafine is an antifungal medication belonging to the class of allylamines. Its mechanism of action involves inhibiting the synthesis of ergosterol, which is a vital component of fungal cell membranes. This results in the accumulation of squalene, causing cell membrane disruption and ultimately fungal cell death.
Butenafine is indicated for the topical treatment of tinea (pityriasis) versicolor due to Malassezia furfur.
Butenafine should be applied topically to the affected area once daily for 7 days. Sufficient Cream should be applied to cover affected areas and extending 4 inches (10.2 cm) onto normal skin immediately surrounding the affected area. Efficacy at greater than 12 g /day has not been established. If a patient shows no improvement in scaling or erythema after the treatment period, the diagnosis and therapy should be reviewed.
Rarely some adverse reaction may a[[ear with the use of Butenafine. These reactions included-
- burning
- stinging
- itching
- Butenafine should be used with caution in patients with a known history of sensitivity to any of its components.
- Avoid contact with eyes, nose, mouth, and other mucous membranes.
- Use of butenafine during pregnancy and lactation should only be done if the potential benefits outweigh the risks.
- If an allergic reaction occurs, discontinue use of the medication and consult a healthcare provider.
Contraindication
Butenafine is contraindicated in patients who are hypersensitive to any of its components.
None known.
None known.
 Bangla
Bangla English
English