| Name | Sodium Stibogluconate |
| Classes |
Antiinfective Agent Antiprotozoal / Amebicide |
| Diseases |
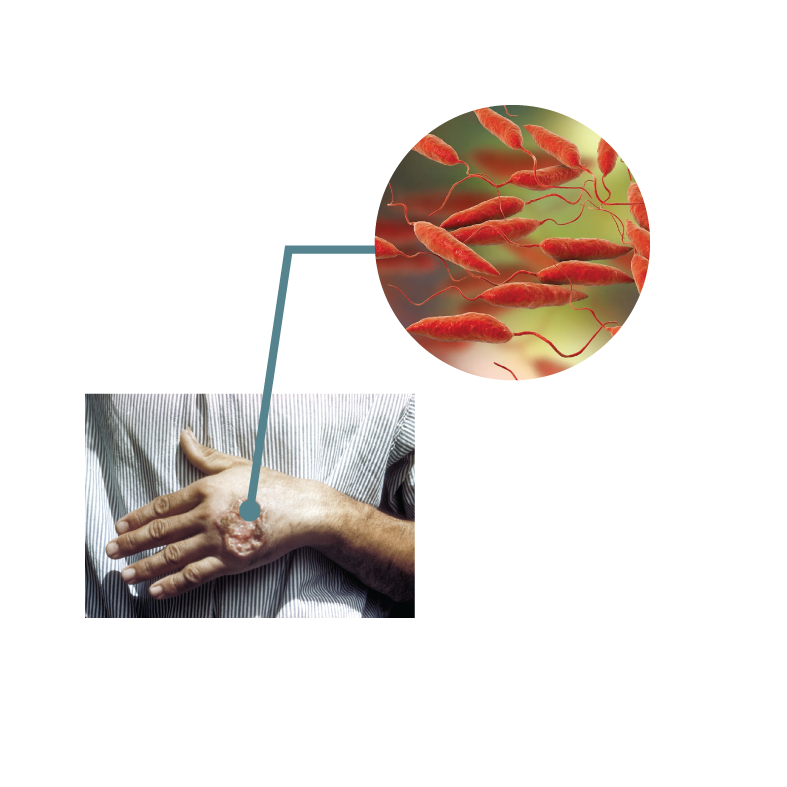
Infectious Disease Leishmaniasis |
Sodium Stibogluconate
Stibogluconate is an antiprotozoal and antimonial drug. The exact mechanism of action is not fully understood. It is believed to work by inhibiting the growth and multiplication of certain parasites, particularly Leishmania species, which cause leishmaniasis.
- Sodium Stibogluconate is indicated for the treatment of leishmaniasis, a parasitic infection caused by Leishmania species transmitted through the bite of infected sandflies.
- It is used for both cutaneous and visceral leishmaniasis, depending on the strain of the parasite and the clinical presentation of the disease.
- The dosage and administration of Sodium Stibogluconate are based on the severity of the leishmaniasis infection, patient's weight, and the specific Leishmania species involved.
- The usual dose is 20mg/kg/day up to 850mg per day given via the IV or IM route for up to 1 month.
- Sodium stibogluconate is exceedingly toxic to veins. One of the practical problems is that after a few doses it can become exceedingly difficult to find a vein in which to inject the drug. The insertion of a PICC does not prevent the problem and can instead exacerbate it: the entire vein along the course of the PICC line can become inflamed and thrombose. Large doses of sodium stibogluconate are often administered as dilute solutions.
- Pancreatitis is a common deleterious effect of the drug, and the serum amylase or lipase should be monitored twice weekly: there is no need to stop treatment if the amylase remains less than four times the upper limit of normal; if the amylase rises above the cut-off, then treatment should be interrupted until the amylase falls to less than twice the upper limit of normal, whereupon treatment can be resumed. Cardiac conduction disturbances are less common, but ECG monitoring while the medicine is injected is advisable and changes quickly reverse after the drug is stopped or the infusion rate is decreased.
- The drug can be given intramuscularly but is exceedingly painful when given by this route. It can also be given intralesionally when treating cutaneous leishmaniasis (i.e., injected directly into the area of infected skin) and again, this is exceedingly painful and does not give results superior to intravenous administration.
- Sodium stibogluconate can also cause a reduced appetite, metallic taste in mouth, nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, headache, tiredness, joint pains, muscle aches, dizziness. and anaphylaxis.
Before using Sodium Stibogluconate, the following points should be considered:
- The drug may cause serious adverse reactions, and patients should be monitored regularly during treatment.
- Liver function tests and electrolyte levels should be regularly checked, especially in patients with pre-existing liver or kidney conditions.
- It is essential to monitor for signs of anemia, as Sodium Stibogluconate can cause hemolytic anemia in some cases.
- If severe adverse reactions occur, the drug should be discontinued, and alternative treatment options should be considered.
Contraindication
Sodium Stibogluconate is contraindicated in patients with a history of hypersensitivity or severe allergic reactions to antimony-containing compounds.
None known.
- Sodium Stibogluconate is contraindicated in patients with severe renal impairment.
- It is also not recommended for use in breastfeeding patients.
 Bangla
Bangla English
English