| Name | Sodium Hydrogen Carbonate |
| Classes |
Antacid Gastrointestinal Agent |
| Diseases |
Bicarbonates Deficiency Electrolytic Imbalance Intoxification Metabolic Acidosis Stomach Upset |
Sodium Hydrogen Carbonate
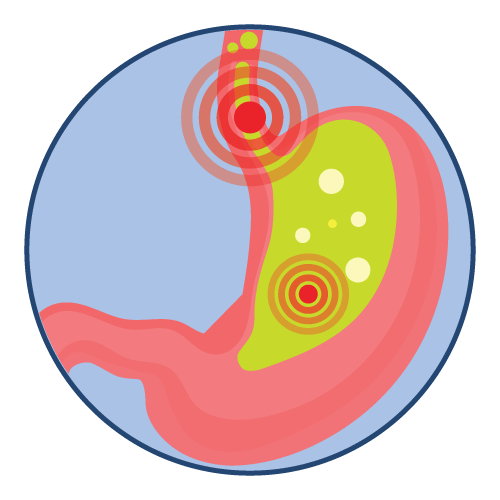
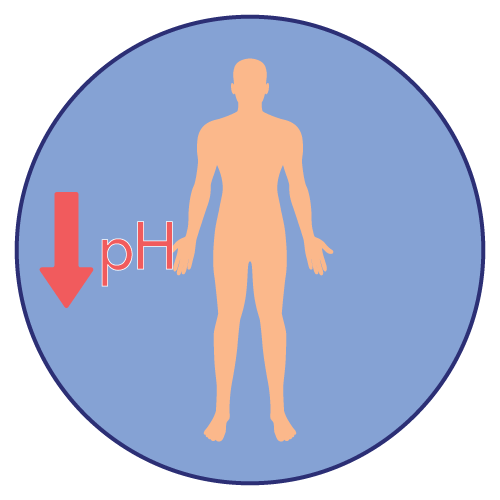
Hydrogen Carbonate (also known as Sodium Bicarbonate) is an alkalizing agent and antacid. Sodium Hydrogen Carbonate works by neutralizing excess acid in the body. It reacts with acidic substances to form water, carbon dioxide, and a salt, thereby raising the pH and reducing acidity.
- Sodium Hydrogen Carbonate is indicated for the treatment of conditions characterized by excess stomach acid, such as acid indigestion, heartburn, and sour stomach.
- It may also be used to alleviate symptoms associated with peptic ulcers, gastritis, and esophagitis.
- It is also used as an urine alkalizer and in metabolic acidosis.
- Oral: The usual dose is 300 mg to 2 grams, 1 to 4 times daily.
- Intravenous (Severe metabolic acidosis):
- Adult: By slow injection of a hypertonic solution of up to 8.4% (1000 mmol/L), or by continuous infusion of a weaker solution, usually 1.26% (150 mmol/L). For correction of acidosis during advanced cardiac life support procedures, 50 ml of an 8.4% solution may be given.
Elderly: Dosage adjustments may be required.
Adverse reactions associated with Sodium Hydrogen Carbonate are generally rare and usually occur with high doses or prolonged use. The following adverse reactions have been reported:
- Abdominal discomfort or bloating
- Belching or gas
- Nausea or vomiting
- Thirst or dry mouth
- Headache
- Alkalosis (elevated blood pH) with prolonged or excessive use
- Sodium Hydrogen Carbonate should be used with caution in individuals with underlying medical conditions, such as kidney disease, heart failure, liver cirrhosis, or high blood pressure.
- Prolonged or excessive use of Sodium Hydrogen Carbonate can lead to metabolic alkalosis, which may manifest as symptoms such as confusion, muscle twitching, or irregular heartbeat. In such cases, medical attention should be sought.
- Patients with a history of sodium-restricted diets should be cautious when using Sodium Hydrogen Carbonate, as it contains sodium.
- Sodium Hydrogen Carbonate may interact with certain medications, such as aspirin or diuretics. Patients should consult with a healthcare professional if they are taking other medications.
Contraindication
Sodium Hydrogen Carbonate is contraindicated in individuals with known hypersensitivity or allergic reactions to the drug or any of its components.
None known.
It should be used with caution in patients with severe renal impairment or metabolic alkalosis.
 Bangla
Bangla English
English