| Name | Sodium Fusidate |
| Classes |
Antiinfective Agent Antibiotic |
| Diseases |
Infectious Disease Osteomyelitis |
Sodium Fusidate
Sodium fusidate is an antibacterial drug that is used to prevent and treat mild to moderate infections caused by bacteria that are susceptible.
Sodium Fusidate is indicated in the treatment of all staphylococcal infections due to susceptible organisms such as:
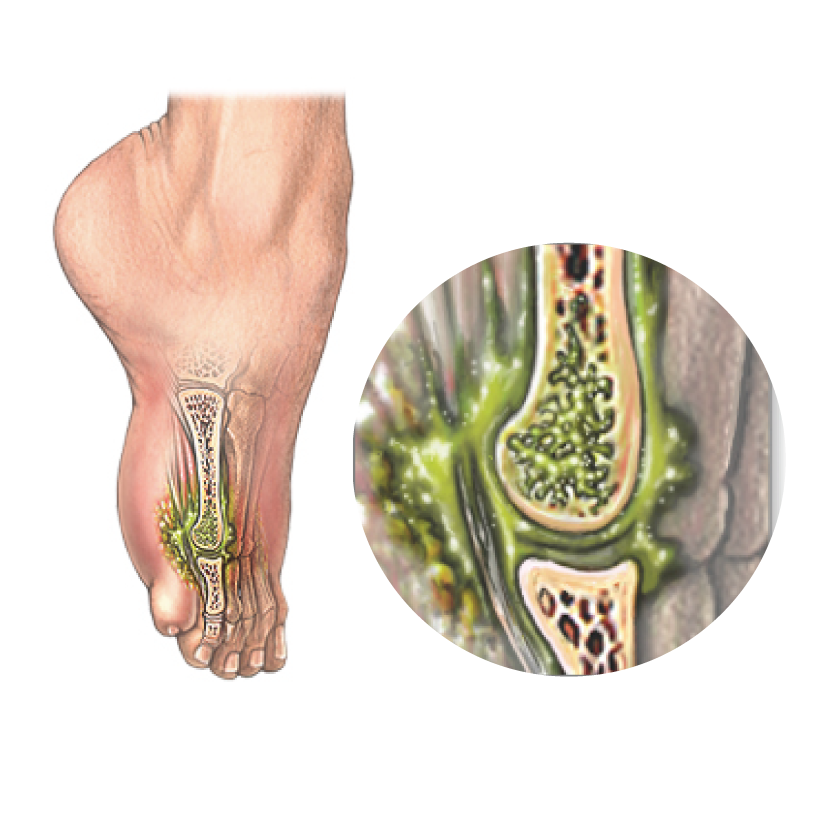
- osteomyelitis
- pneumonia
- septicemia
- wound infections
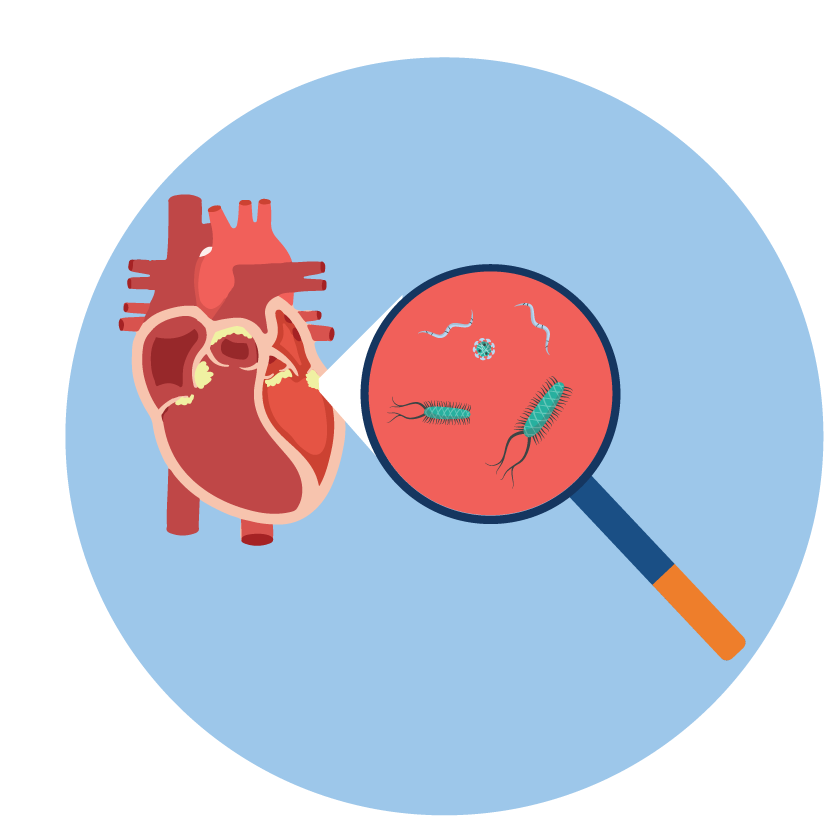
- endocarditis
- superinfected cystic fibrosis
- cutaneous infections
- eye infection
- bacterial conjunctivitis
- keratitis
Sodium fusidate is available as cream, suspension and ophthalmic drops.
Topical/Cutaneous
Skin infections
- Adult: Apply 3-4 times per day to the affected region till it improves. If a gauze dressing is utilized, the number of times it is applied each day can be reduced to 1-2.
- Child: As a 2% ointment, cream, or gel: Apply 3-4 times per day to the affected region till it improves. If a gauze dressing is utilized, the number of times it is applied each day can be reduced to 1-2.
Oral
Susceptible infections
- Adult: 500 mg thrice a day. May be up titrated to 1 g thrice a day in severe infections.
- Child: <1 year 6mg/kg; 1-5 years 250 mg; 5-12 years 500 mg; >12 years Same as adult dose. Doses to be taken thrice a day.
Intravenous
Susceptible infections
- Adults weighing more than 50 kg: 500 mg sodium fusidate three times daily.
- Children and adults weighing less than 50 kg: 6-7 mg sodium fusidate per kg bodyweight three times daily.
Commonly associated side effects when administered orally/sytemically include-
- Vomiting
- Diarrhoea
- Abdominal pain
- Dyspepsia
- Nausea
- Abdominal discomfort
- Liver problems
- Jaundice
- Hepatitis
- Systemic sodium fusidate and statins (HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors) should not be taken together. Rhabdomyolysis (including fatalities) has been reported in people receiving this combination.
- With systemic Fucidin, significant cutaneous responses placing lives at risk have been documented, including Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS) syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis (Lyell's syndrome), and Stevens-Johnson syndrome.
- The liver metabolizes sodium fusidate which is then expelled in the bile. Elevated liver enzymes and jaundice have been reported with systemic Fucidin therapy, however these side effects are usually reversible once the medicine is stopped.
- The usage of fusidic acid has been linked to the development of bacterial resistance. Extensive or recurrent use of antibiotics, like with all drugs, increases the chance of acquiring antibiotic resistance.
Contraindication
- Contraindicated in patients hypersensitive to fusidic acid.
- Statins should not be co-administered with fusidic acid.
There is no known contraindications of fusidic acid in terms of food and drinks.
There's no known contraindication of the drug in terms of health.
 Bangla
Bangla English
English