| Name | Sodium Citrate |
| Classes |
Uninary pH Modefier |
| Diseases |
Electrolytic Imbalance Kidney Stone Metabolic Acidosis |
Sodium Citrate
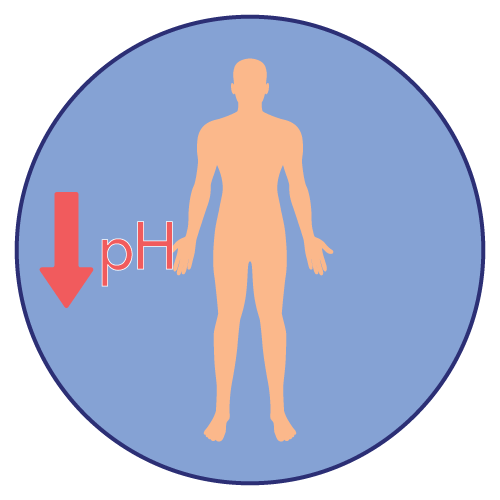
Sodium citrate is a urinary alkalinizing agent. It works by neutralizing excess acid in the urine and maintaining a proper acid-base balance. It is a sodium salt of citric acid, which dissociates in the urine to provide sodium ions that combine with hydrogen ions, lowering the urine's acidity.
Sodium citrate is indicated for the treatment of:
- Urinary tract infections
- Urolithiasis (stones in the urinary tract)
- Gout
- Metabolic acidosis
The dosage of sodium citrate varies based on the indication and the patient's condition. It is available in different strengths and formulations, including tablets, solution, and powder. The recommended dosage and administration should be determined by a healthcare provider.
Adverse reactions with the use of sodium citrate are rare. However, it may cause side effects such as nausea, vomiting, abdominal discomfort, diarrhea, muscle twitching, and muscle weakness.
- Sodium citrate should be used with caution in patients with renal impairment or congestive heart failure, as excessive sodium intake may lead to fluid overload or exacerbation of these conditions.
- It should be used with caution in patients on a sodium-restricted diet or with a history of hypertension or edema.
- Use of sodium citrate may increase the risk of urinary tract infections caused by urea-splitting bacteria.
- Sodium citrate should not be used in patients with severe renal insufficiency, hypernatremia, or metabolic alkalosis.
- Long-term use of sodium citrate may lead to systemic alkalosis, which can lead to muscle weakness, respiratory depression, and cardiac arrhythmias.
Contraindication
Sodium citrate is contraindicated in patients with Hypersensitivity to sodium citrate or any of its components
None known.
Sodium citrate is contraindicated in patients with-
- Severe renal insufficiency
- Hypernatremia
- Metabolic alkalosis
- Patients with Addison's disease, aldosteronism, or other conditions associated with hyperkalemia
 Bangla
Bangla English
English