| Name | Sodium Acetate |
| Classes |
Electrolyte and Mineral Nutritional Supplement |
| Diseases |
Electrolytic Imbalance Hyponatremia (Low Sodium) |
Sodium Acetate
Sodium Acetate dissociates in water, releasing sodium ions (Na+) and acetate ions (CH3COO-). Sodium ions play a crucial role in maintaining fluid and electrolyte balance in the body, while acetate ions can be metabolized in the liver to produce bicarbonate ions, which helps in buffering acidosis.
- The dosage and administration of Sodium Acetate should be individualized based on the patient's condition, electrolyte levels, and the healthcare provider's judgment.
- It is typically administered intravenously under medical supervision. The rate of administration and total volume should be determined based on the patient's specific needs.
Adverse reactions associated with Sodium Acetate may include:
- Hypernatremia (elevated sodium levels in the blood)
- Hypokalemia (low potassium levels in the blood)
- Hyperchloremia (elevated chloride levels in the blood)
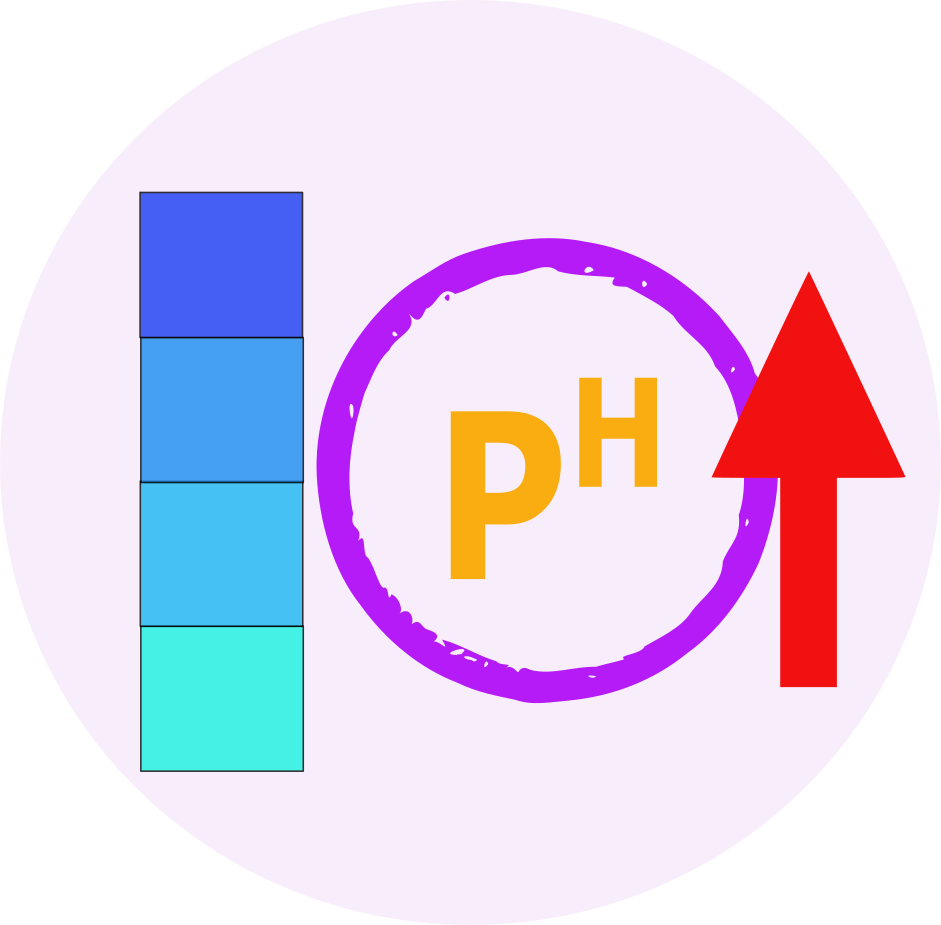
- Metabolic alkalosis (elevated pH and bicarbonate levels in the blood)
- Fluid overload (excessive accumulation of fluid in the body)
- Sodium Acetate should be used with caution in patients with heart failure, edema, or conditions that may predispose them to fluid retention.
- It should be administered with caution in patients with renal impairment or electrolyte imbalances, as it may affect fluid and electrolyte balance.
- Regular monitoring of electrolyte levels, particularly sodium, potassium, and chloride, is essential during treatment with Sodium Acetate.
- Rapid infusion of Sodium Acetate may lead to hypernatremia or fluid overload; it should be administered at a rate appropriate for the patient's clinical condition.
- Special caution should be exercised when administering Sodium Acetate to patients with impaired hepatic function or severe liver disease.
Contraindication
Contraindicated in patients hypersensitive to any component of the formulation.
None known.
- Sodium Acetate is contraindicated in patients with severe renal impairment or anuria (absence of urine production).
- It should not be used in patients with severe electrolyte disturbances, such as hypernatremia or hyperchloremia.
 Bangla
Bangla English
English