| Name | Salsalate |
| Classes |
Analgesic / Pain Killer Central Nervous System Agent Salicylate |
| Diseases |
Arthritis Inflammatory Disease |
Salsalate
Salsalate is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) with analgesic and antipyretic properties. Its mechanism of action involves the inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis, primarily through the inhibition of cyclooxygenase (COX) enzymes. Salsalate is classified as a salicylate.
Salsalate is indicated for the treatment of:
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: To reduce signs and symptoms.
- Osteoarthritis: To alleviate pain and inflammation.
- Mild to Moderate Pain: For relief of mild to moderate pain.
-
Rheumatoid Arthritis and Osteoarthritis:
- Adults: The initial dosage is typically 1500 mg to 3000 mg daily, administered in divided doses. Adjustments may be made based on individual response.
- Pediatric Patients: Safety and efficacy in pediatric populations have not been established.
-
Mild to Moderate Pain:
- Adults: The recommended dosage is usually 1000 mg to 2000 mg every 12 hours.
Adverse reactions are listed from most common to least common:
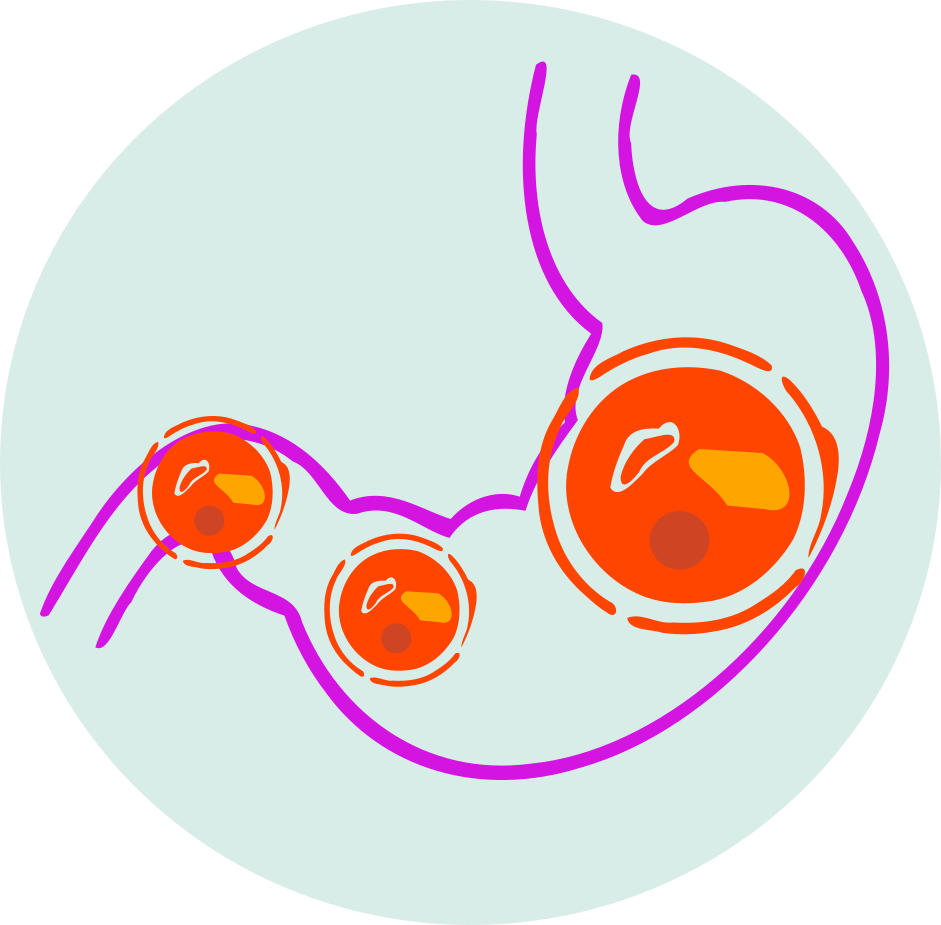
- Gastrointestinal disturbances (e.g., dyspepsia)
- Tinnitus or hearing impairment
- Hypersensitivity reactions (e.g., rash)
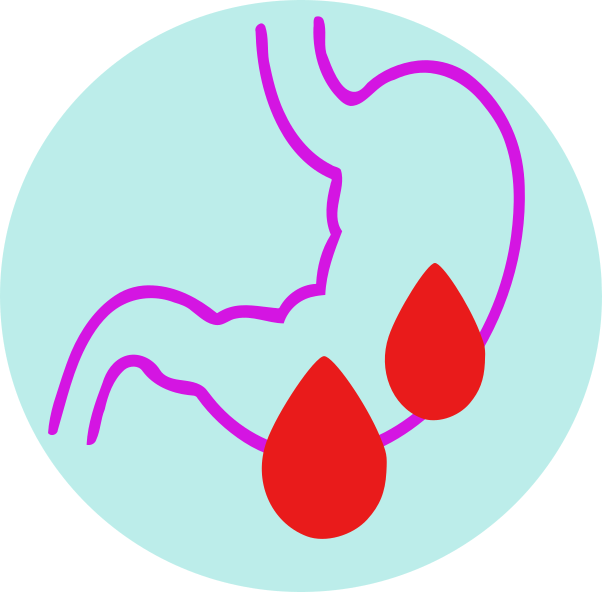
- Gastrointestinal bleeding
- Gastrointestinal Effects: Salsalate can cause gastrointestinal bleeding and ulcers; caution in patients with a history of peptic ulcer disease.
- Renal Effects: Monitor renal function, especially in patients with pre-existing renal conditions.
- Hypersensitivity Reactions: Discontinue salsalate if hypersensitivity reactions occur.
Contraindication
Salsalate is contraindicated in:
- Patients with a known hypersensitivity to salicylates such as-
None known.
Salsalate is contraindicated in-
- Patients with active peptic ulcer disease or a history of gastrointestinal bleeding.
- Pediatric patients with varicella or influenza-like illnesses.
 Bangla
Bangla English
English